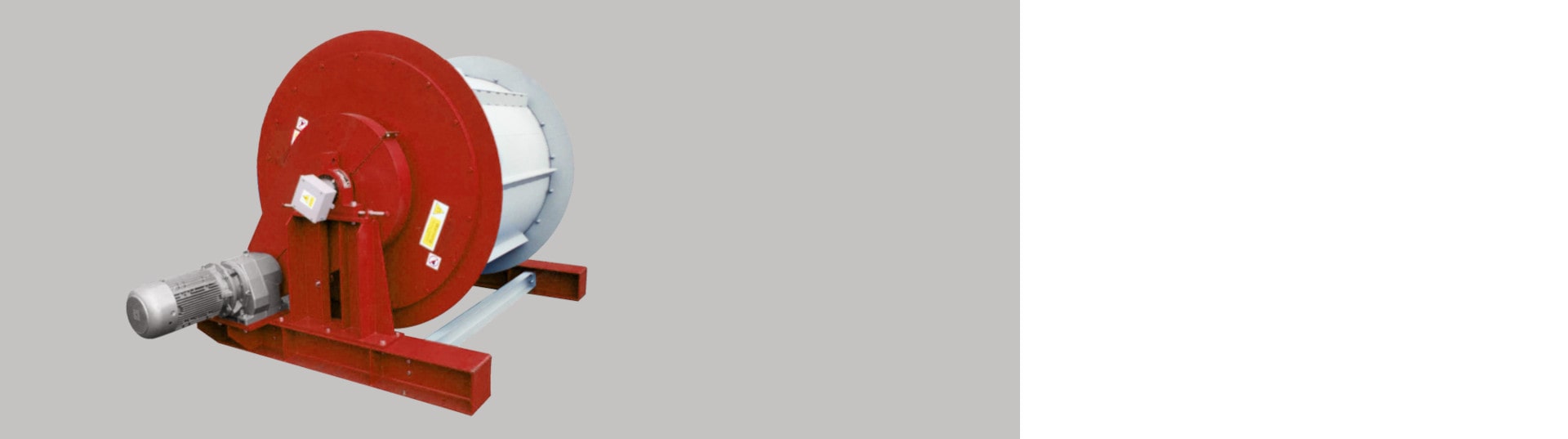Electromagnetic drum MB E
Electromagnetic drum is a device for automatic and permanent removal of magnetic iron metals from inert materials. In case of highly abrasive materials or if there are present sharp objects in the material, the magnetic drum can be a suitable substitution for e. g. an overband magnet. The electro drums have no dead spots and their magnetic attractive force is stronger than a permanent design. That is why the electromagnetic drums are preferable for the separation of larger sized and heavier ferrous metals and are used above all for cleaning shredded scrap and cars, incineration bottom ash, foundry residues etc. Besides, when there is a high material layer, high magnetic forces are needed to extract the ferrous metal from the non-metallic material - and the electro drums are able to cope with this task. And for applications where the magnetic drum requires switching off, the only option is the electro magnet, where the magnetic field is easily switched on and off.
Benefits for the use of separator
- Final material without iron contamination
- Protection of production equipment
- Smooth production operation
- Automatic cleaning without interruption of the material flow
- Elimination of operator errors
Separator design
The electro drum magnet has stationary electromagnetic coils positioned inside a non-magnetic, commonly manganese steel shell, fitted with welded stainless-steel wiper bars. The shell rotates around the stationary electromagnetic coil at a speed determined by the volume of processed material.
Transformer rectifier
Transformer rectifier provides power to the magnet at the correct Amps, depending on magnet design, ambient temperature and input voltage.
Transformer rectifier design
- Fully welded steel enclosure to IP 65
- Oil level gauge fitted to front of tank
- Transformer: double wound transformer to BS EN 60076
- Rectifier according to BS 4417 ABCD
- Protection: diode protection with fast acting semi-conductor fuses
Application modes
Material can be fed onto the drum at one of three different points depending on process configuration:
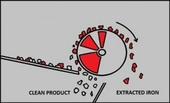
- The material is fed onto the top of the electro drum. Magnetic material is attracted and held to the drum shell before being discharged beneath the drum. This kind of feeding is ideal for the application of MB E RADIAL.
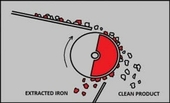
- The material is fed onto to the centre of the electro drum. Attracted magnetic material is discharged opposite to the in feed. MB E AXIAL as well as MB E RADIAL can be applied.
- The material is fed beneath the electro drum. Magnetic material is captured and held to the drum shell and then carried up and discharged over the top of the drum. This kind of feeding is ideal for the application of MB E AXIAL.
In all three configurations, non-magnetic materials will free-fall forward following their normal trajectory.
- Several magnetic poles aligned parallely to the axis
- Continuous high field strength at the separation zone
- Even cover wear
- High-intensity primary coil for the concentration of the maximum flux at the point of extraction
- Lower intensity secondary coil for the transport of the ferrous material to the point of discharge
- Ducted coils extend the coil life
- Heavy duty design
- Platewheel is bolted to a robust drive ring
- Extensive optional equipment (spillage rings, base frame, geared motor, chain drive, split platewheel)
MB E AXIAL is set with several magnetic poles aligned parallely to the axis of the drum. The first pole is extremely strong and attracts the incoming material, the other poles are used to retain the ferrous particles on the drum surface before the ferrous metals is discharged. MB E AXIAL drums are designed to allow extracted magnetic materials to flip (because of different polarity) over the face of the drum to release any non-metallic materials that may be caught between the ferrous material and the magnet. This kind of electromagnetic drum is used in applications such as municipal refuse and automobile fragmentiser plants (in order to achieve the best possible ferrous purity). Non-magnetic materials are unaffected and flow under a normal trajectory.
- Several poles are arranged radially over the width of the drum
- Electromagnetic coils concentrate maximum flux at the point of extraction
- Extension pole arranges for the discharge
- High processing capacity
- Platewheel is bolted to a robust drive ring
- Extensive optional equipment (spillage rings, base frame, geared motor, chain drive, split platewheel)
MB E RADIAL is set with radial pole (all coils have the same polarity and are placed next to each other, giving a continuous radial polarity over the entire width of the drum). The strong magnetic field attracts the magnetically susceptible materials to the rotating shell surface of the drum. The revolving shell transports the magnetic particles by means of an extension pole out of the magnetic field where they are discharged into a collection area or onto a receiving conveyor. Non-magnetic materials are unaffected and flow under a normal trajectory.
Which industrial branches can the electro magnetic drum be use of in?
Electromagnetic drums offered by SOLLAU are made in co-operation with a renowned European producer in order to be used in difficult and arduous environments including automobile and vehicle fragmentation plants, household waste incineration plants, household refuse recycling operations, steelworks recovering steel from slag etc.

Recycling and waste processing

Machining and foundry industry

Paper industry

Tobacco industry

Ceramic and glass industry

Mining and quarrying industry

Cement and lime industry

Chemical industry, paints and lacquers

Automotive industry

Plastics and rubber industries

Thermal power plants

Wood industry